The Renovation Wave (RW) initiative has been designed by the European Union (EU) to tackle the dual problem of economic growth and energy saving in the building sector. In particular, it aims to double the annual energy renovation rate throughout the EU by 2030 and to foster deep energy renovations. As a result, such interventions could inevitably not only stimulate economic growth by creating new jobs and new demands for renovation but also foster the EU’s contribution to sustainable development goals (SDGs) through the implementation of Sustainable Energy and Climate Action Plans (SECAPs) before 2030.
As part of the LOCALISED project, researchers at CMCC in collaboration with IREC, PIK, IMP, and Julich developed a framework for analysing RW programs in four selected countries: Italy, Spain, Poland, and Germany. They analysed information including duration of the program, funding size, target groups (designated recipients), coverage (national or regional), and as a conclusion, whether the adoption of these programs leads to structural change or not. Table 1 shows the comparative statistics about the RW programs in each country. As shown here, most programs in these 4 countries are short-term (1-3 years) with medium budget (between 201 and 999 million of Euro) and targeted towards municipalities as the main recipient.
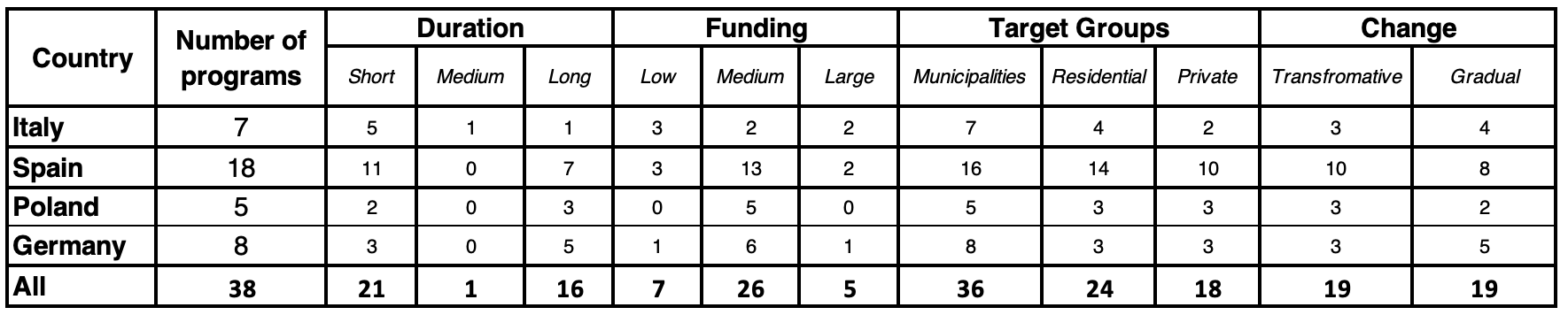
Table 1: general information about the programs
Next, researchers focused on specific interventions in each program and tried to link them to the LOCALISED Mitigation/Adaptation database, and also to relevant sustainable development goals (SDGs) and Sustainable Energy and Climate Action Plans (SECAPs) initiatives through specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
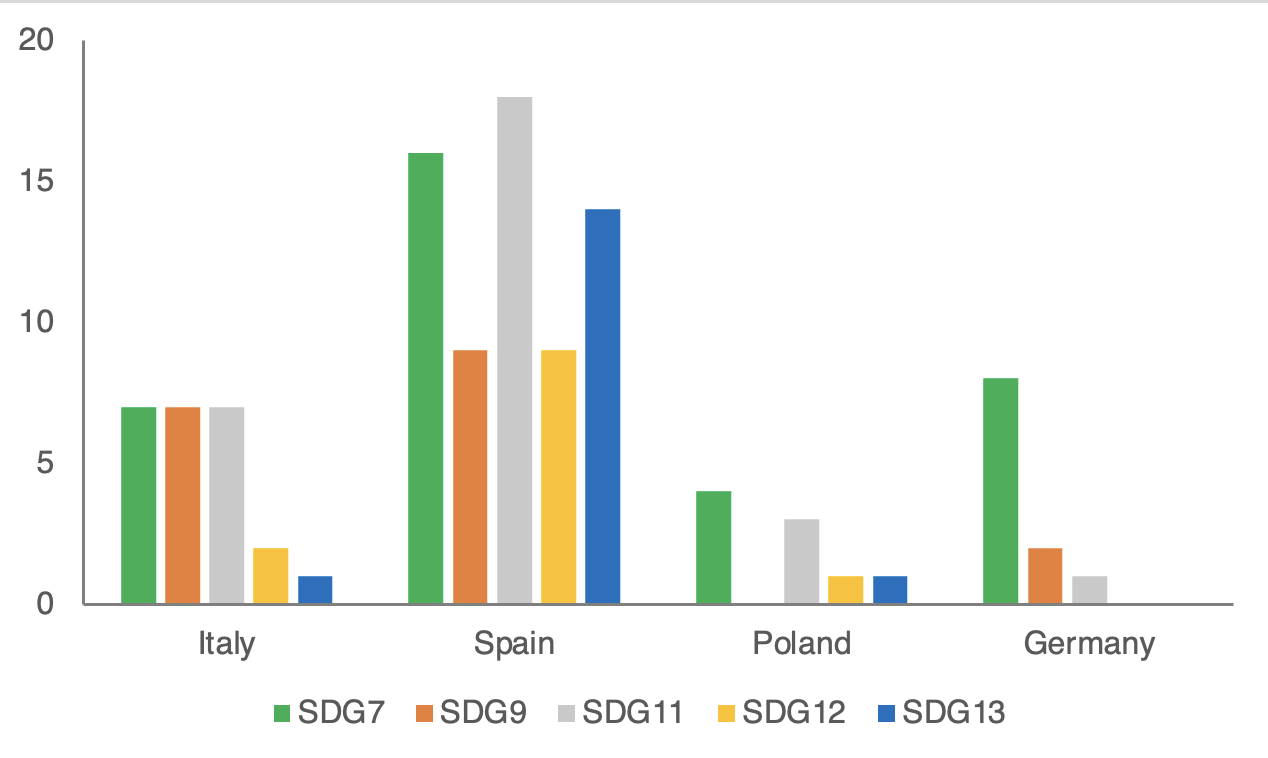
Figure 1: the most frequent SDGs per country
The findings of this research summarised in Figure 1, indicate that Renovation Wave programs at the national level offer a strong link to SDGs and specifically SDG 7 which aims at ensuring access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy, is present in 92% of the analysed programs.
The two other commonly linked SDGs (SDG 11 and SDG 9) focus on making cities and human settlements, building resilient infrastructure, promoting sustainable industrialization, and fostering innovation.
In terms of SECAP KPIs (Figure 2), it’s been shown that mitigation pillar (24%), energy consumption pillar (22%) and energy poverty pillar (19%) can be identified as the ones most relevant to the national RW programs.
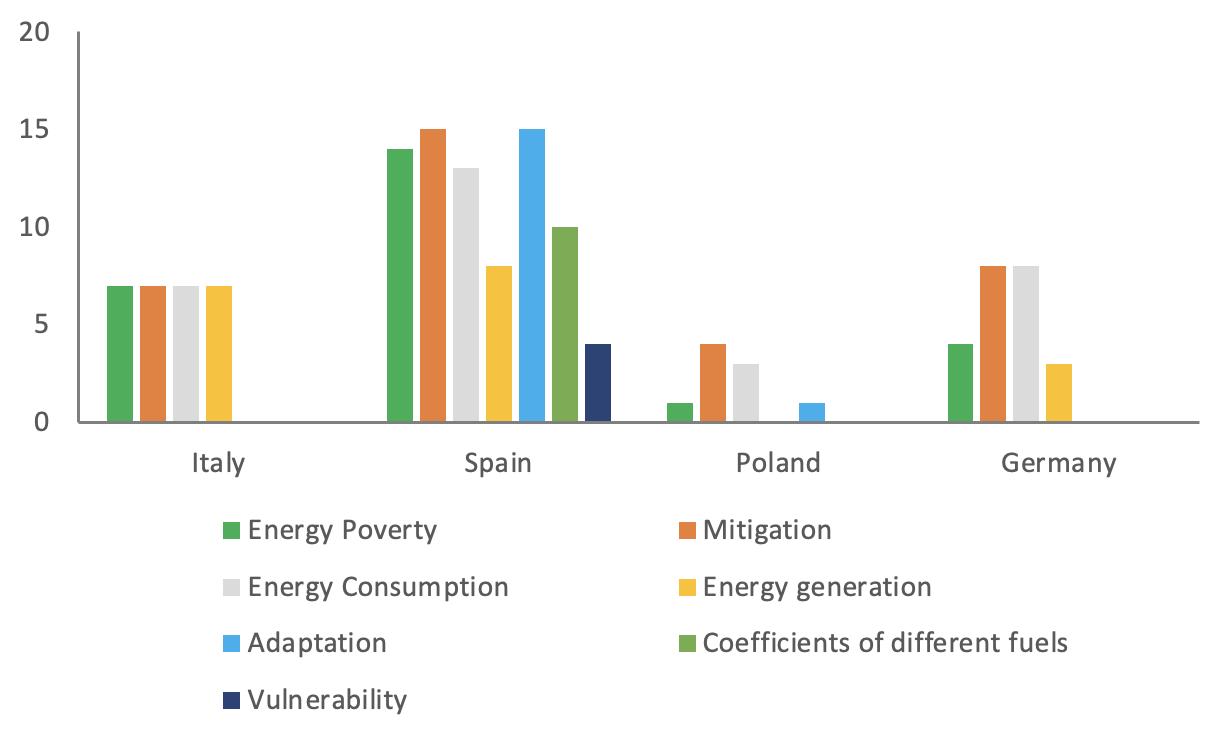
Figure 2: the most frequent SECAPs per country

Recent Comments