A commonly held perspective, endorsed by scientists, policymakers, and the public at large, asserts that tackling the climate crisis and promoting sustainable development must be interconnected. To facilitate a shift toward a green global economy while still enabling ongoing economic growth, substantial changes in the structure of global production and consumption are necessary. Nevertheless, the specifics of resource reallocation—how and where it should occur—remain contingent upon the assumptions made regarding the pace of the green transition.
A recent paper—by our LOCALISED partner CMCC—explores three transition scenarios, each characterised by the pace of the shift from a fossil-fuel-based economy (brown) to a renewable energy-dominated one (green). These scenarios include a constant (linear) transition, a rapid transition, and a delayed transition. The paper analyses the demands of each pathway in terms of reallocating capital and labour, as well as investing in capital stocks and research and development (R&D). Through this analysis, one can identify key factors influencing various transition paths and inform overall policy priorities.
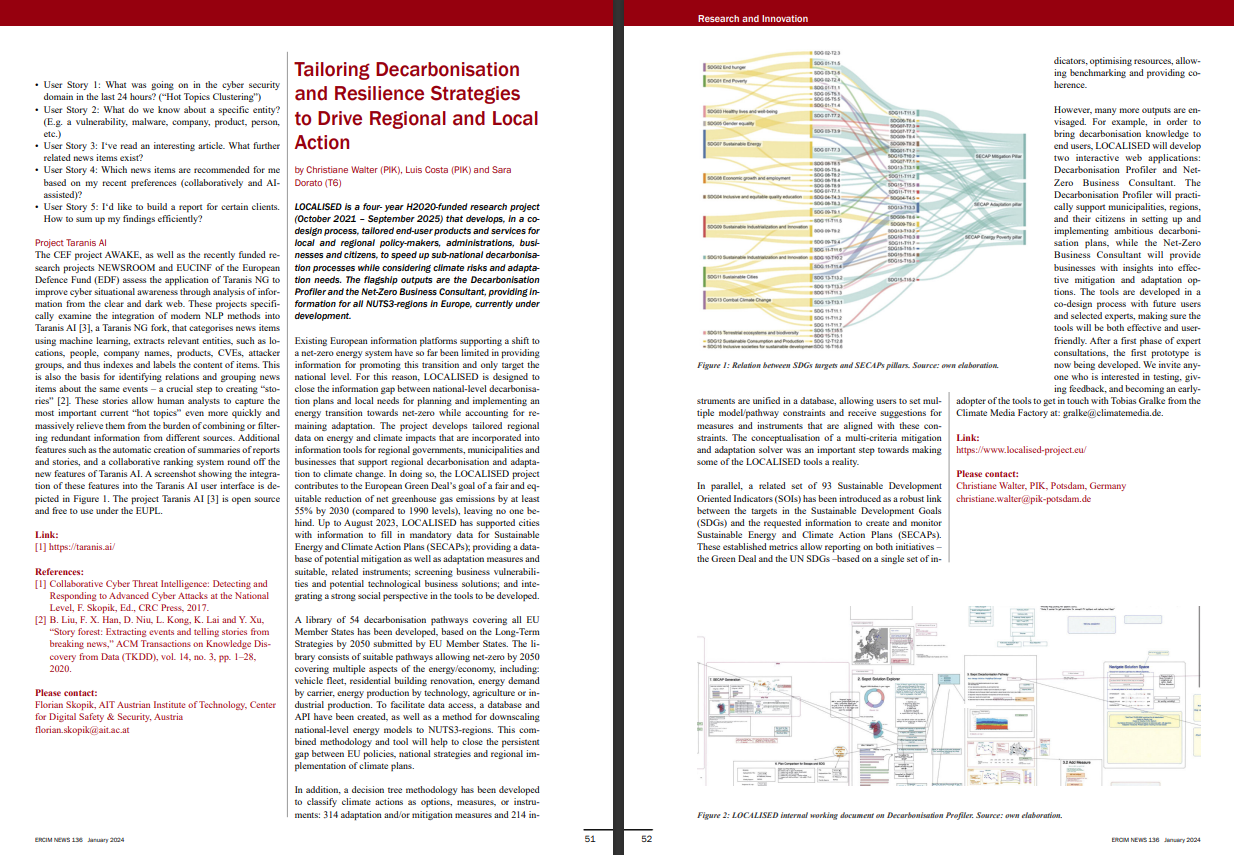
This paper builds on a widely used integrated assessment model of climate change and economy and introduces several important changes and additions that enable the representation of the green transition in a simplified but relevant manner. Specifically, our model, shown in the figure above, has two productive sectors, one “green” and one “brown”. Capital and labour can be moved between these two sectors at a certain cost. Moreover, long-term productivity growth depends on R&D investments which must be allocated between the two sectors.
Comparing different transition pathways, the first implication of the speed of the transition is for the trajectory of CO2 emissions where fast transition entails deeper and earlier reduction of the emissions while the other pathways reduce emissions more gradually. Across scenarios, transitions are achieved through different combinations of factor transfers from the “brown” to the “green” sector and investments in green capital stocks and R&D. In particular, the fast transition pathway relies very heavily on transfers of capital from the “brown” to the “green” sector with labour reallocation being comparatively more limited and homogeneous across scenarios. The fast pathway also requires substantial emission abatement efforts in the “brown” sector, which results in a sharp decline in emissions. The slower pathways, meanwhile, feature a larger amount of investment and capital accumulation generated within the “green” sector itself, hence avoiding a part of the cost associated with reallocating capital across sectors.






Recent Comments